A V6 engine is a six-cylinder internal combustion engine with the cylinders arranged in a V-shaped configuration, typically set at a 60° or 90° angle. It’s a popular engine design used in many mid-size and performance vehicles due to its balance of power, efficiency, and compact size.
Each side of the "V" holds three cylinders, and the crankshaft is shared between both banks. This configuration provides smoother operation and more compact packaging compared to inline-6 engines, making it ideal for front-wheel-drive and rear-wheel-drive layouts.
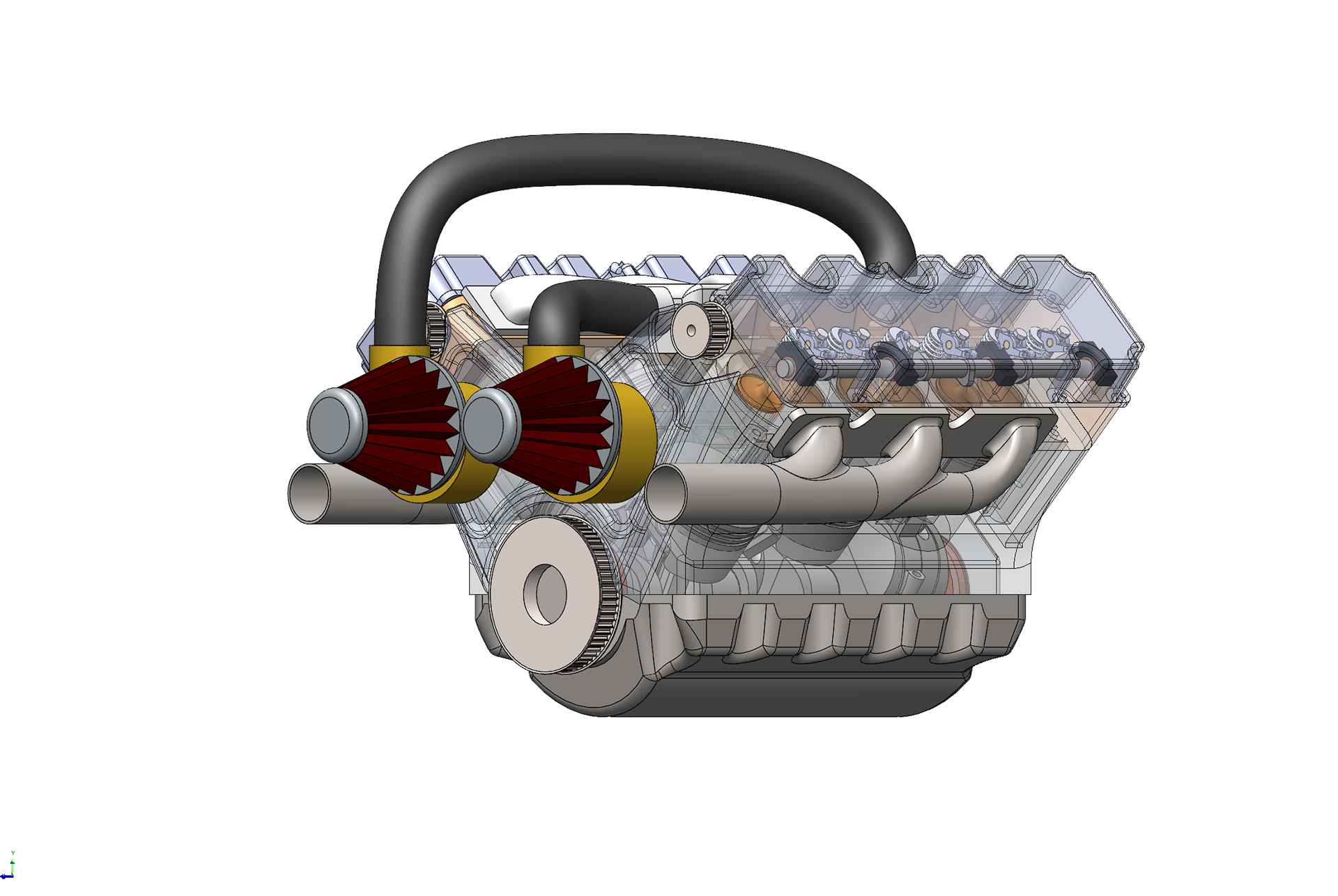
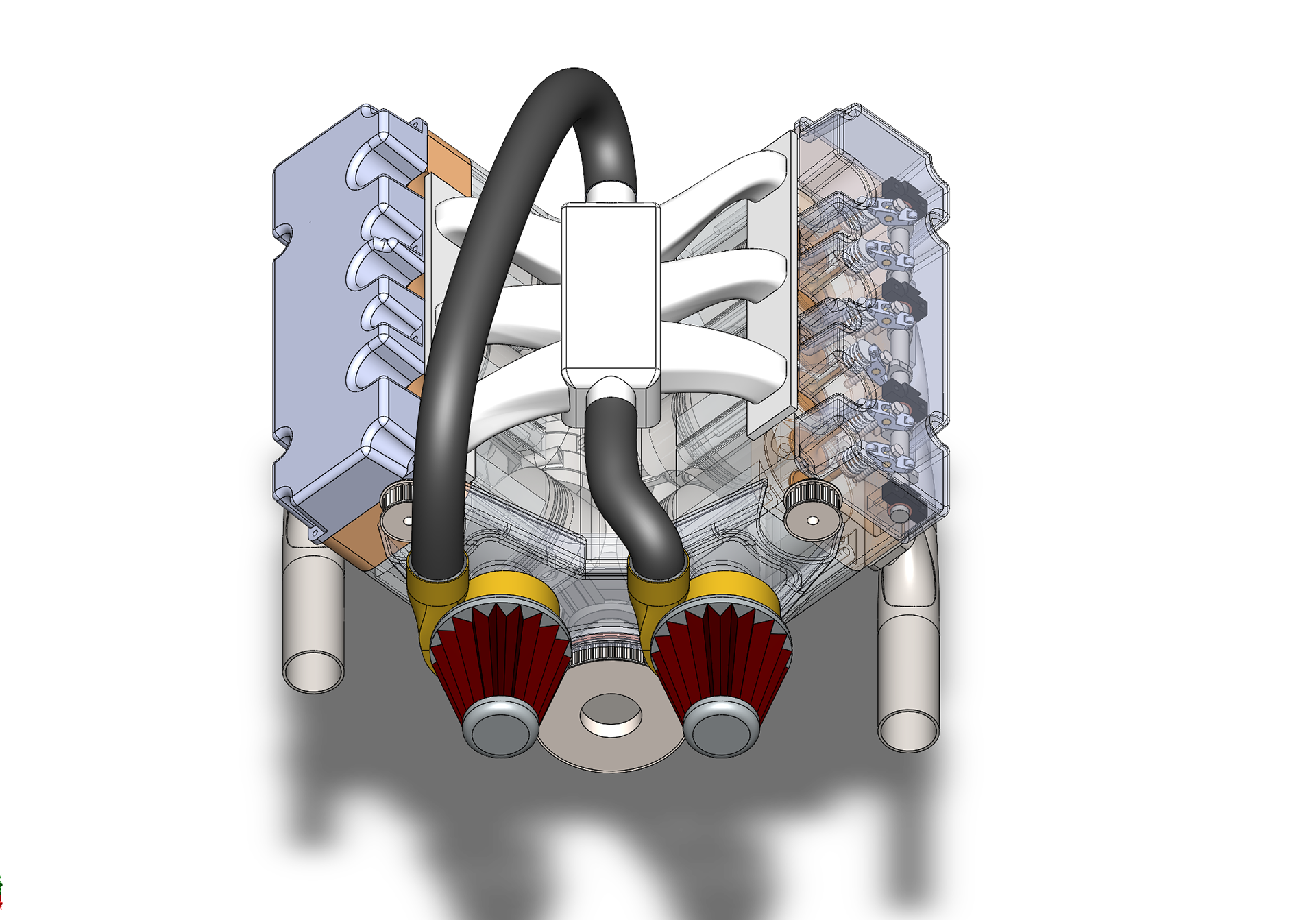
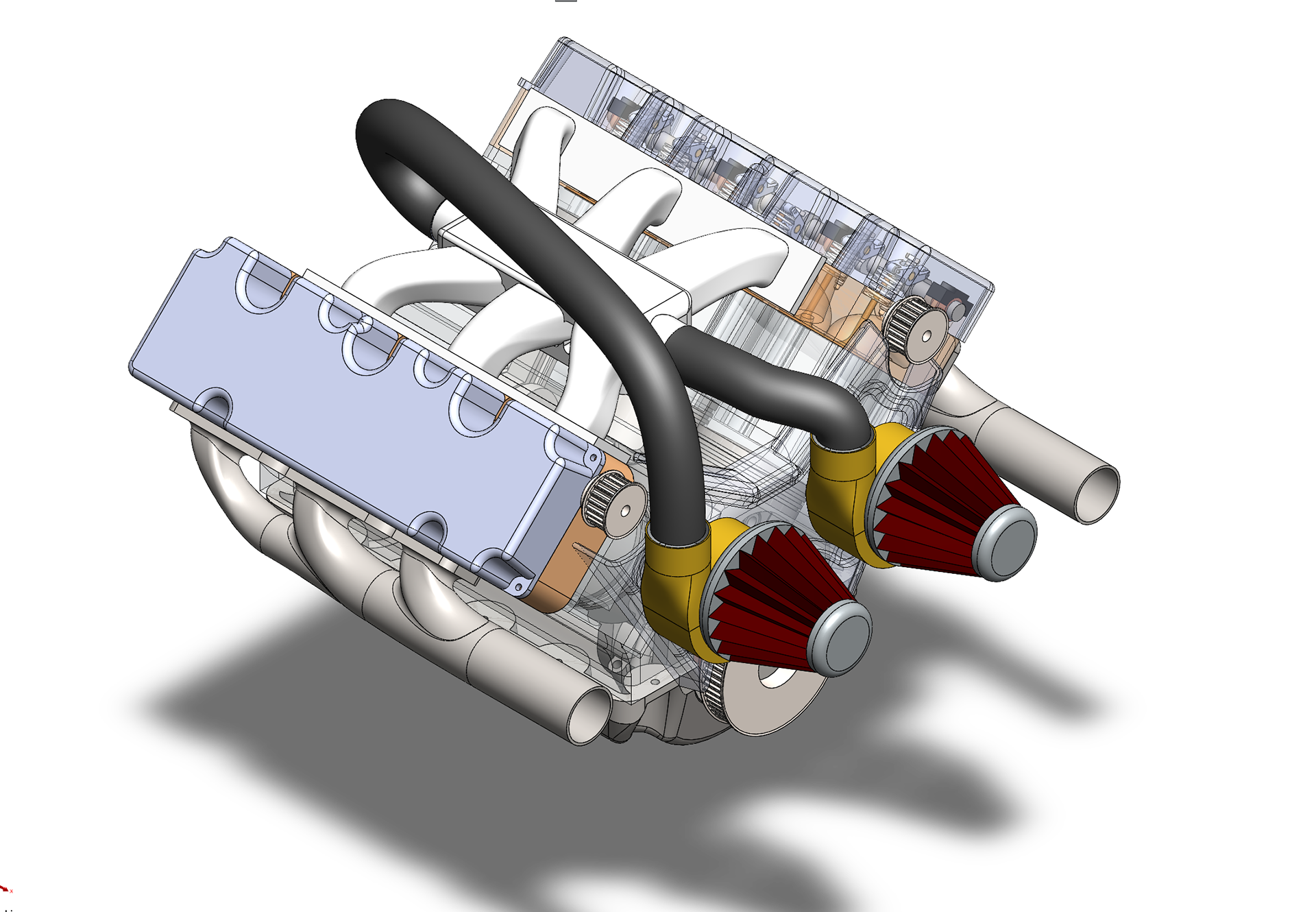
A V6 engine is a six-cylinder internal combustion engine where the cylinders are arranged in two banks of three, forming a "V" shape. It operates on the four-stroke cycle — intake, compression, power, and exhaust — in which each piston draws in a fuel-air mixture, compresses it, ignites it with a spark, and expels the exhaust gases. These strokes occur in a carefully timed sequence across all six cylinders to ensure smooth, balanced power delivery. As the pistons move up and down, they rotate a crankshaft, converting linear motion into rotational energy that powers the vehicle. The camshaft, synchronized by a timing chain or belt, controls the opening and closing of the intake and exhaust valves. The V configuration makes the engine more compact than an inline-six, allowing for easier packaging in modern engine bays while maintaining strong performance and efficiency. Widely used in passenger cars, SUVs, and performance vehicles, the V6 strikes an excellent balance between power, refinement, and space efficiency.